Supabase Installation
Set up pg_track_events to work with Supabase
Supabase Installation
We recommend setting up pg_track_events inside a backend repository, where you already have a Supabase project connected.
If you do not have one alreayd, add an .env.local file to your project with a DATABASE_URL variable. As we'll be modifying the database, you will want to use a connection string that authenticated the postgres user Supabase creates.
You can find your connection string by clicking "Connect" in the top of the UI.

After you click "Connect", you'll be able to copy the connection string. Make sure to choose the "Session Pooler" option (the 3rd one):

Initialize in your backend
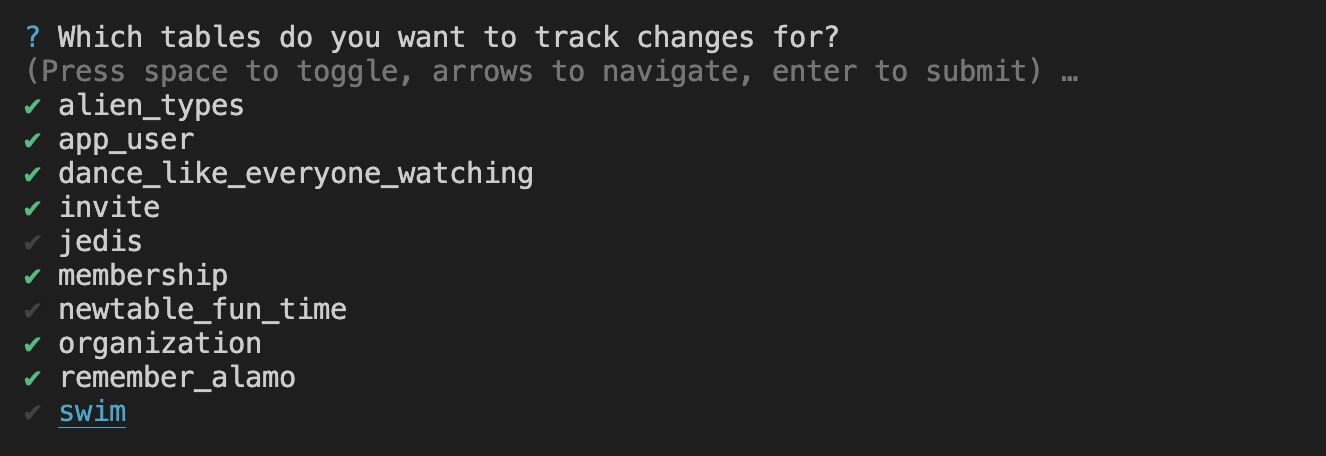
Select tables you wish to track
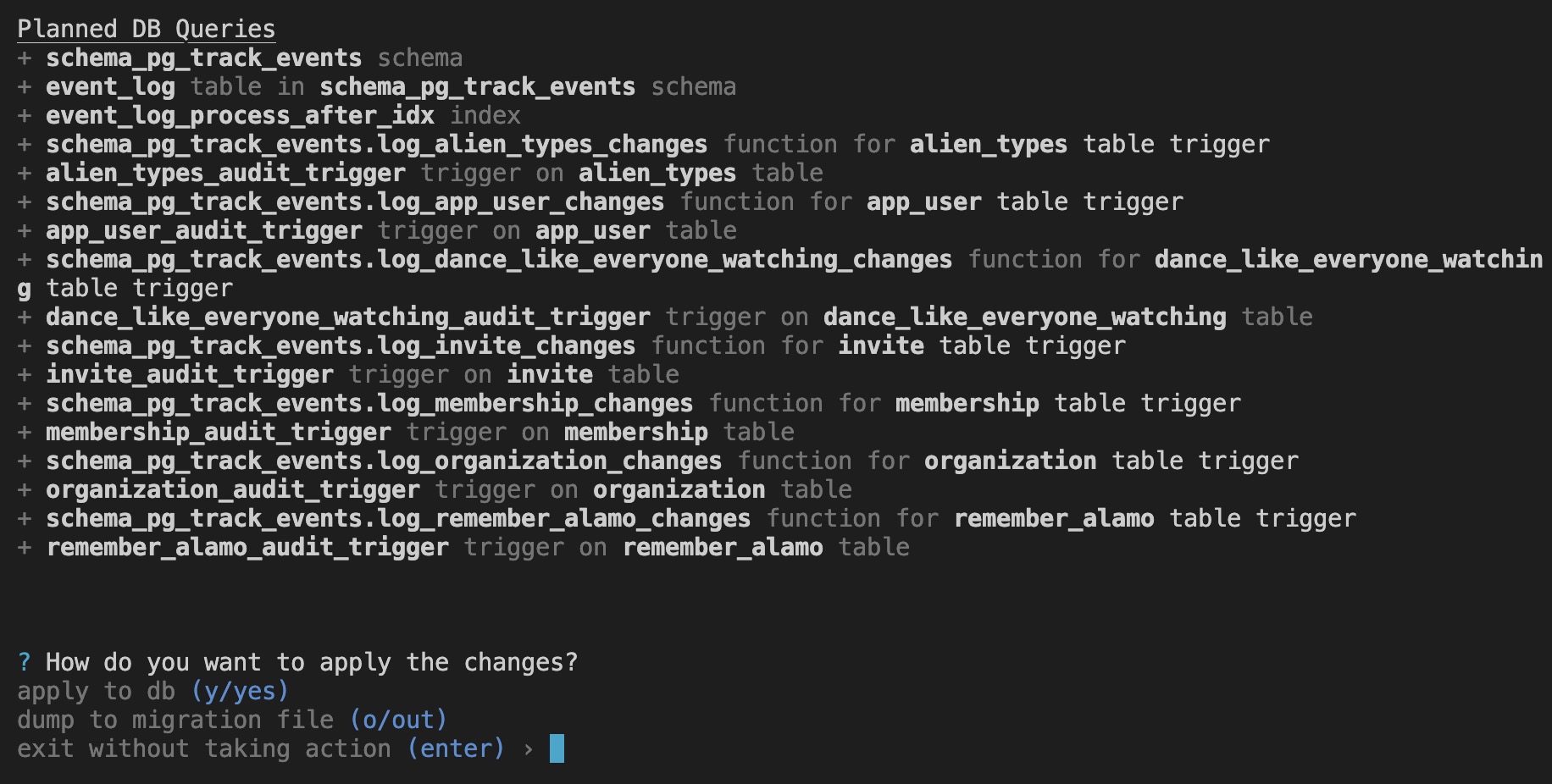
The CLI will output the triggers, functions and tables it plans to add.
Configure Tracked Events
Add your own trackers and configure destinations in the pg_track_events.config.yamlfile.
Full instructions here
Deploy a worker
Deploy a worker to your infrastructure. The Docker container created by init command should be ready to build and deploy, but you can customize it if you need to. Full docs here
Watch the events flow!